North Carolina's congressional districts


North Carolina is currently divided into 14 congressional districts, each represented by a member of the United States House of Representatives. After the 2000 census, the number of North Carolina's seats was increased from 12 to 13 due to the state's increase in population. In the 2022 elections, per the 2020 United States census, North Carolina gained one new congressional seat for a total of 14.[1]
Current districts and representatives
[edit]List of members of the United States House delegation from North Carolina, their terms, their district boundaries, and the district political ratings according to the CPVI. The delegation has a total of 14 members, with 7 Republicans, and 7 Democrats.
| Current U.S. representatives from North Carolina | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | Member (Residence)[2] |
Party | Incumbent since | CPVI (2022)[3] |
District map |
| 1st |  Don Davis (Snow Hill) |
Democratic | January 3, 2023 | D+2 | 
|
| 2nd |  Deborah Ross (Raleigh) |
Democratic | January 3, 2021 | D+12 | 
|
| 3rd |  Greg Murphy (Greenville) |
Republican | September 17, 2019 | R+15 | 
|
| 4th |  Valerie Foushee (Hillsborough) |
Democratic | January 3, 2023 | D+16 | 
|
| 5th |  Virginia Foxx (Banner Elk) |
Republican | January 3, 2005 | R+13 | 
|
| 6th |  Kathy Manning (Greensboro) |
Democratic | January 3, 2021 | D+4 | 
|
| 7th |  David Rouzer (Wilmington) |
Republican | January 3, 2015 | R+8 | 
|
| 8th |  Dan Bishop (Waxhaw) |
Republican | September 17, 2019 | R+20 | 
|
| 9th |  Richard Hudson (Southern Pines) |
Republican | January 3, 2013 | R+6 | 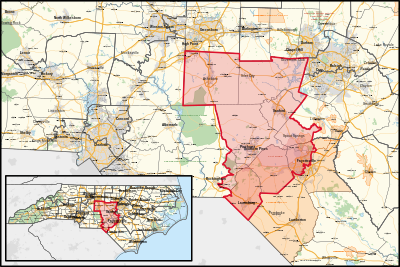
|
| 10th |  Patrick McHenry (Lake Norman of Catawba) |
Republican | January 3, 2005 | R+22 | 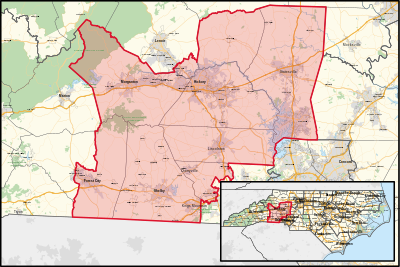
|
| 11th |  Chuck Edwards (Flat Rock) |
Republican | January 3, 2023 | R+8 | 
|
| 12th |  Alma Adams (Charlotte) |
Democratic | November 4, 2014 | D+13 | 
|
| 13th |  Wiley Nickel (Cary) |
Democratic | January 3, 2023 | R+2 | 
|
| 14th | Vacant | December 31, 2024 | D+6 | 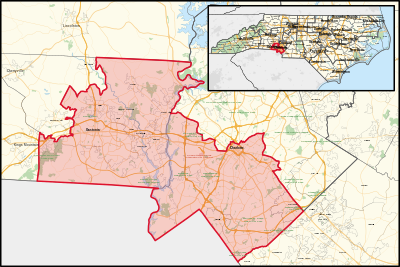
| |
Legal challenges to redistricting
[edit]1981 redistricting
[edit]In 1981, the North Carolina General Assembly proposed a congressional redistricting plan that split Moore County between two districts, the first time a county in North Carolina had ever been thus divided. The Attorney General of North Carolina recommended revising the plan.[4]
Constitutionality of the 1990 redistricting
[edit]After the 1990 census, the US Department of Justice directed North Carolina under VRA preclearance to submit a map with two majority-minority districts. The resultant map with two such congressional districts, the 1st and 12th, was the subject of lawsuits by voters who claimed that it was an illegal racial gerrymander. A three-judge panel of the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of North Carolina dismissed the suit, which was appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court. On June 28, 1993, the U.S. Supreme Court, in Shaw v. Reno, found that the 12th congressional district was an unlawful racial gerrymander. Justice Sandra Day O'Connor's opinion found that if a district's shape, like the 12th's, was "so bizarre on its face that it is 'unexplainable on grounds other than race'", that it would be subject to strict scrutiny as a racial gerrymander, and remanded the case to the Eastern District of North Carolina.
On August 22, 1994, the Eastern District of North Carolina on remand in Shaw v. Hunt found that the 12th congressional district was a racial gerrymander (as the U.S. Supreme Court had directed), but ruled that the map satisfied strict scrutiny due to the compelling interest of compliance with the Voting Rights Act and increasing black political power.[5] This was again appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court, which reversed the Eastern District of North Carolina on June 13, 1996, and found that the North Carolina plan violated the Equal Protection Clause and that the 12th congressional district did not satisfy a compelling interest.[6]
Constitutionality of the 1997 redistricting
[edit]North Carolina drew a new map following Shaw v. Hunt, and the new maps were challenged in turn. A three-judge panel of the Eastern District of North Carolina granted summary judgment that the new boundaries were an illegal racial gerrymander.[7] This was appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court, which in Hunt v. Cromartie on May 17, 1999, unanimously ruled that the Eastern District of North Carolina was in error to grant summary judgment and remanded the case for the court to hold a trial.
After the ensuing trial, the Eastern District of North Carolina ruled that the 12th district was an illegal racial gerrymander on March 7, 2000.[8] This was again appealed, now as Easley v. Cromartie. The U.S. Supreme Court on April 18, 2001, reversed the Eastern District of North Carolina and ruled that the 12th district boundaries were not racially based but was a partisan gerrymander. They said this was a political question that the courts should not rule upon. Justice O'Connor, the author of Shaw v. Hunt, was the swing justice who switched sides to uphold the district boundaries.
Constitutionality of the 2010 redistricting
[edit]In February 2016, a three-judge panel of U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit and Middle District of North Carolina judges ruled that the 1st and 12th congressional districts' boundaries were unconstitutional and required new maps to be drawn by the legislature to be used for the 2016 election.[9] On 22 May 2017, the U.S. Supreme Court, in Cooper v. Harris, agreed that the 1st and 12th congressional district boundaries were unlawful racial gerrymanders, the latest in a series of cases dating back to 1993 by different parties challenging various configurations of those districts since their first creation.[10][11]
In January 2018 a federal court struck down North Carolina's congressional map, declaring it unconstitutionally gerrymandered to favor Republican candidates. The court ordered that the General Assembly must redraw the district maps prior to the 2018 elections.[12] However, the U.S. Supreme Court stayed the federal court order pending review,[13] and in June 2019, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in Rucho v. Common Cause, by a 5–4 vote, that partisan gerrymandering is a "political question" that the federal courts have no place to rule on.[14][15]
Constitutionality of the 2017 redistricting
[edit]
On September 3, 2019, a three-judge panel in a 357-page ruling unanimously struck down the Republican-led state legislature drawn 2017 enacted maps,[17] which were drawn to replace the 2011 maps which were also ruled unconstitutional and thrown out on racial grounds.[18] The court ruled that the state House and state Senate districts maps were such an extreme partisan gerrymander that they violated the state constitution. In the ruling the state legislature was ordered by the court to immediately start drawing new maps; the court demanded that they be drawn based on criteria like population, contiguity, and county lines. Districts had to be drawn without "partisan considerations and election results data," and done so in plain view, a departure from the closed-door processes the ruling eschews. "At a minimum, that would require all map drawing to occur at public hearings, with any relevant computer screen visible to legislators and public observers." The judges said the new maps had to be completed in two weeks; they also said they reserved the right to move the 2020 primary election if needed.[19]
In October 2019, a panel of three judges ruled that the map was an unfair partisan gerrymander and had to be redrawn.[20] On November 15, 2019, the General Assembly passed a bill that drew new districts that were used for the 2020 elections. The 2nd and 6th congressional districts were drawn to be more favorable to Democrats under the new proposal.[21] On December 2, 2019, a three-judge panel ruled that newly Republican-drawn congressional district maps completed in November 2019 would stand for federal elections in 2020. The maps allowed to stay in place would only be used once. After the 2020 census, the congressional districts would have to be redrawn again.[22]
Constitutionality of the 2020 redistricting
[edit]On February 4, 2022, the North Carolina Supreme Court struck down the congressional and state legislative district maps drawn by the GOP-controlled General Assembly as an unconstitutional partisan gerrymander in a 4–3 ruling, after a testimony had shown that Republicans were likely to win 10 out of 14 U.S. House seats under the proposed map, an increase from the eight out of 13 that they won in the 2020 elections. New maps, which were ordered to be fair in partisan composition, had to be drawn by the General Assembly within two weeks, under state law.[23]
On February 23, 2022, a panel of three former judges chosen by the Wake County Superior Court drew and approved a new remedial congressional map after the court, earlier that day, struck down the congressional district maps passed by the General Assembly on February 17, 2022, as not meeting standards of partisan fairness. The new maps, which were upheld by the North Carolina Supreme Court later in the night, would apply for the 2022 elections. The General Assembly would then be able to redraw new congressional maps for use in 2024 and subsequent elections until new maps will have to be redrawn for 2032.[24][25]
Later developments
[edit]On April 28, 2023, the North Carolina Supreme Court—after Republicans gained a majority in the court following the 2022 judicial elections—overturned the same ruling in a 5–2 decision, which cleared the way for gerrymandering in the next redistricting cycle.[26][27] On October 25, 2023, new maps were approved by the General Assembly. All three new maps heavily favor the GOP, with allegations of racial bias made against the maps as well. Compared to the congressional map used in the 2022 elections, the GOP is expected to at least gain three seats in the House.[28][29][30]
In December 2023, two lawsuit were filed in the Middle District of North Carolina, with the first challenging the 1st, 6th, 12th, and 14th congressional districts in the map,[31][32] and the second, challenging multiple specific districts in the congressional and state legislative district maps, as racial gerrymanders.[33][34][35] Both lawsuits were consolidated together in March 2024.[36][37]
Historical and present district boundaries
[edit]Table of United States congressional district boundary maps in the State of North Carolina, presented chronologically.[38] All redistricting events that took place in North Carolina between 1973 and 2013 are shown, congressional composition is listed on the right.
See also
[edit]- United States congressional delegations from North Carolina
- List of United States congressional districts
- North Carolina Democratic Party
- North Carolina Republican Party
- Shaw v. Reno, landmark Supreme Court case relating to gerrymandering
- Rucho v. Common Cause, another Supreme Court gerrymandering case relating to North Carolina's congressional map
References
[edit]- ^ Merica, Dan; Stark, Liz (April 26, 2021). "Census Bureau announces 331 million people in US, Texas will add two congressional seats". CNN. Retrieved April 26, 2021.
- ^ "Office of the Clerk, U.S. House of Representatives". clerk.house.gov. Retrieved January 6, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Cook PVI: District Map and List". The Cook Political Report. July 12, 2022. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ Powell, William S.; Criner, Allyson C. (2006). "Civil Rights Movement Part 6: Continued Civil Rights Battles in the State". NCPedia. North Carolina Government & Heritage Library. Retrieved December 11, 2022.
- ^ "Shaw v. Hunt, 861 F. Supp. 408 (E.D.N.C. 1994)". Justia Law. Retrieved August 1, 2023.
- ^ "Shaw v. Hunt, 517 U.S. 899 (1996)". Justia Law. Retrieved September 28, 2023.
- ^ "Cromartie v. Hunt, 34 F. Supp. 2d 1029 (E.D.N.C. 1998)".
- ^ "Cromartie v. Hunt, 133 F. Supp. 2d 407 (E.D.N.C. 2000)".
- ^ Blythe, Anne (February 5, 2016). "Federal court invalidates maps of two NC congressional districts". The Charlotte Observer. Archived from the original on September 29, 2019. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ "Supreme Court tosses Republican-drawn North Carolina voting districts". Reuters. May 22, 2017. Archived from the original on May 22, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2019.
- ^ Stern, Mark Joseph (May 22, 2017). "In Cooper v. Harris, the Supreme Court strikes a blow against racial redistricting". Slate Magazine. Archived from the original on October 29, 2019. Retrieved October 29, 2019.
- ^ a b Blinder, Alan (January 9, 2018). "North Carolina Congressional Map Ruled Unconstitutionally Gerrymandered". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved January 9, 2018.
- ^ "Supreme Court Blocks Redrawing of North Carolina Congressional Maps". Reuters. Retrieved January 20, 2018.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (June 27, 2019). "Supreme Court Says Constitution Does Not Bar Partisan Gerrymandering". The New York Times. Retrieved June 27, 2019.
- ^ Supreme Court of the United States supremecourt.gov
- ^ "North Carolina General Assembly - 2016 Contingent Congressional Plan - Corrected*". Archived from the original on April 16, 2016.
- ^ "Common Cause v. Representative David R Lewis, et al. Judgement" (PDF). CommonCause.org. September 5, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- ^ Doran, Will (September 3, 2019). "After maps struck down in NC gerrymandering lawsuit, top Republican leader won't appeal". Herald Sun. Retrieved September 7, 2019.
- ^ Timm, Jane C. (September 4, 2019). "North Carolina judges slam GOP gerrymandering in stinging ruling, reject district maps". NBC News. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- ^ Williams, Pete (August 28, 2019). "Court throws out North Carolina's congressional district maps". NBC News. Archived from the original on October 29, 2019. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ "House Bill 1029 / SL 2019-249 (2019-2020 Session) - North Carolina General Assembly". www.ncleg.gov.
- ^ Timm, Jane C. (December 2, 2019). "In blow to North Carolina Democrats, court rules new GOP-drawn voting maps can be used for 2020". NBC News. Retrieved December 3, 2019.
- ^ "NC Supreme Court strikes down redrawn voting maps". WTVD. February 5, 2022. Archived from the original on February 5, 2022. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- ^ Wilkie, Jordan (February 23, 2022). "All sides appeal redistricting decision to NC Supreme Court". Carolina Public Press. Archived from the original on February 24, 2022. Retrieved February 24, 2022.
- ^ Doyle, Steve (February 23, 2022). "Check out new election maps: NC Supreme Court rejects appeals, approves special masters' districts". WGHP. Archived from the original on February 24, 2022. Retrieved February 24, 2022.
- ^ Timm, Jane C. (April 28, 2023). "N.C.'s new GOP-controlled high court reverses itself on gerrymandering and voter ID". NBC News. Retrieved October 25, 2023.
- ^ Zach, Montellaro; Josh, Gerstein; Ally, Mutnick (April 28, 2023). "North Carolina Supreme Court clears way for partisan gerrymandering". POLITICO. Retrieved October 25, 2023.
- ^ Robertson, Gary D. (October 25, 2023). "North Carolina Republicans put exclamation mark on pivotal annual session with redistricting maps". AP News. Retrieved October 26, 2023.
- ^ Lopez, Ashley (October 25, 2023). "North Carolina lawmakers approve maps creating gains for the GOP in Congress". NPR. Retrieved October 26, 2023.
- ^ Schouten, Fredreka; Gallagher, Dianne (October 25, 2023). "North Carolina legislature approves map that could help Republicans gain at least 3 House seats in 2024". CNN Politics. Retrieved October 26, 2023.
- ^ Robertson, Gary D. (December 4, 2023). "New North Carolina congressional districts challenged in federal court on racial bias claims". AP News. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ Gallagher, Dianne (December 5, 2023). "Lawsuit seeks to block North Carolina congressional map, alleging it discriminates against minority voters". CNN Politics. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- ^ Robertson, Gary D. (December 19, 2023). "North Carolina's election maps for 2024 are racially biased, advocates say in lawsuit". AP News. Retrieved January 26, 2024.
- ^ Selzer, Rachel (December 19, 2023). "Civil Rights Groups and Black Voters Sue Over New North Carolina Maps". Democracy Docket. Retrieved January 26, 2024.
- ^ Bonner, Lynn (December 19, 2024). "Voting rights groups file sweeping lawsuit against NC redistricting plans". NC Newsline. Retrieved January 26, 2024.
- ^ "North Carolina Congressional Redistricting Challenge (2023)". Democracy Docket. March 19, 2024. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ "North Carolina 2023 Redistricting Challenge". Democracy Docket. March 19, 2024. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ "Digital Boundary Definitions of United States Congressional Districts, 1789–2012". Retrieved October 18, 2014.
External links
[edit]- Rose Institute of State and Local Government, "North Carolina: 2010 Redistricting Changes", Redistricting by State, Claremont, CA: Claremont McKenna College



















